
Open access is the emerging standard for how scientific literature is published and shared. An open access publication is digital, has no fees required for access, and has no copyright or licensing restrictions. The idea is to make scientific findings accessible to all who would benefit. This is a noble goal, but the practicalities of its application can be confusing. There are a number of ways that authors and publishers can make published studies available open access. Some put the burden of payment on the author or institution that produced the research, some on the publisher, and an emerging model puts it on libraries who enter agreements with publishers for subscriptions with open access benefits for researchers at their institution.
The three most common models are green, gold, and diamond/platinum open access. Here’s a quick breakdown of each:
Green OA - A publisher allows the author(s) to self-archive an open access copy of the article being published in one of its journals. This is generally allowed for a preprint version of the article. The author can opt to self-archive to a subject-based archive like PubMed Central, or in an institutional repository, like Himmelfarb’s Health Sciences Research Commons. To find out if a journal allows Green OA and what the specific terms are, Sherpa/Romeo is a free tool to check publisher open access policies. Learn more about how to deposit your research in an institutional repository in our video tutorial, Archiving Scholarship in an Institutional Repository.
Gold OA - The authors (or their affiliated institution) pay the publisher to allow open access to the content with an Article Processing Charge (APC). In this model, the author frequently retains copyright. The downside is the typically high expense to publish gold OA in reputable journals. Note that vanity presses and some predatory publications will fall into the gold category. Learn more about how to identify a predatory journal in our video tutorial, How to Spot a Predatory Journal.
Diamond or Platinum OA - Also known as cooperative or non-commercial open access, in this model neither the author nor the reader pays. Typically this model is used by not-for-profit publishing venues like University presses or scholarly society publications. A 2021 study estimated that there are 29,000 diamond OA journals, but only 10,000 of them are included in the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ), and many are not indexed to make their contents findable in databases. Only about half of diamond OA journal articles have a DOI which jeopardizes future access.
The Venn diagram below developed by Jamie Farquarhson illustrates what each of the three levels means for both authors and readers.
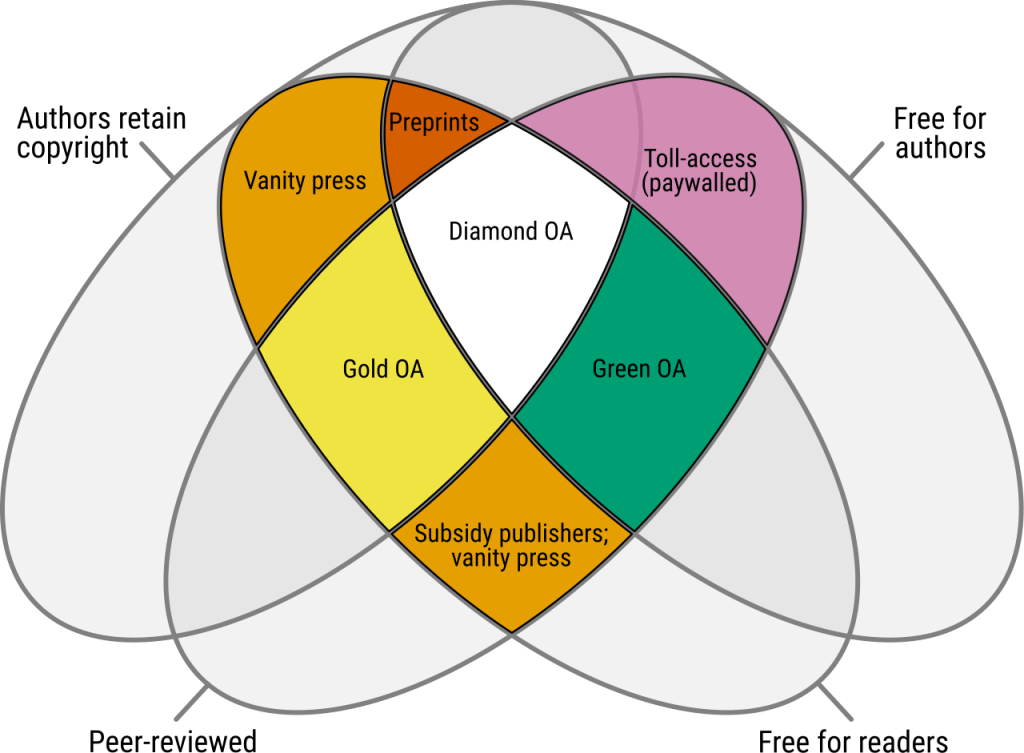
As Gold OA becomes more common, some institutions are creating funds that their researchers can use to pay for APCs. Researchers are also including these expenses in grant applications, especially for those like NIH grants that require depositing research findings and associated data in freely accessible archives. Learn more about how to include article processing charges into grants in our video tutorial, How to Include Article Processing Charges (APCs) in Funding Proposals.
As mentioned earlier in this article, libraries are starting to take on some of the burden of APCs. In what’s known as a transformative agreement, the fees paid to a publisher are transitioning from subscription access for library users to open access publishing by the institution’s researchers and authors. The library pays for both users to read for free and for the institution's authors to publish open access in the publisher’s journals. There may be limits on how many articles can be published or other price caps built in. Usually, these agreements are cost neutral meaning that the library is not saving on subscription fees. Currently, GW has transformative agreements in place with Cambridge Journals and The Company of Biologists (Development, Journal of Cell Science, and the Journal of Experimental Biology). GW has explored transitioning to transformative agreements with other publishers.
Sources
Arianna Becerril, Lars Bjørnshauge, Jeroen Bosman, et al. The OA Diamond Journals Study. March, 2021. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4562790
Lisa Janiche Hinchliffe. Transformative Agreements in Libraries: A Primer. The Scholarly Kitchen blog, April 23, 2019. https://scholarlykitchen.sspnet.org/2019/04/23/transformative-agreements/


