Social engineering - the art of exploiting human psychology, rather than technical hacking techniques, to gain access to buildings, systems, or data.
Cyber attackers manipulate victims (targets) into making poor choices that enables direct and indirect criminal activity
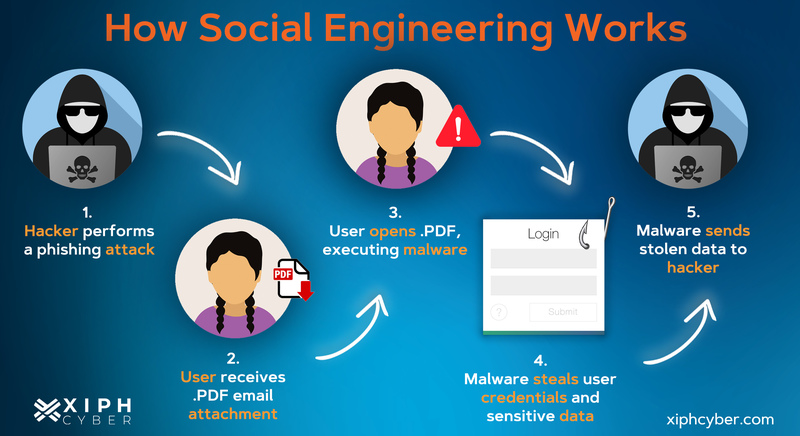
Social Engineering attacks are conducted using various methods. The general process involves an attacker sending messages or otherwise contacting potential victims. Once the attacker has established contact, either directly with a victim responding or indirectly when a victim clicks a link or downloads an attachment, they steal user information such as account credentials, personal information, and funds. In some cases the attacker installs malware on the victims device to steal data as well as use the device to launch attacks against others.
Phishing
Phishing is a very simple and useful tool in an attacker’s arsenal. Phishing can lead to the exposure of sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, PII (personally identifiable information), and credit card information. So what is Phishing? It is at method used to obtain sensitive information from a victim that leverages social engineering and communications technologies that people use every day. There are various methods of phishing, with the most common being email, vishing (voice phishing), and smshing (text phishing). These methods can be blanket attempts that rely on quantity instead of quality (often called campaigns) or they can be very carefully crafted attacks with very specific targets (spear phishing and whaling). Luckily, identifying and defeating these attacks can be simple if you know what to look out for.

Email Phishing
Email is the hacker’s go-to for most phishing attacks; people wouldn’t think twice about receiving an email. Often phishing emails will contain a malicious link, a malware attachment, or directly ask for sensitive information. In order to trick victims, these emails are crafted to appear from a big company, such as FedEx, Apple, or even from inside your own organization. Attackers use look-a-like or spoof emails to convince the target the email is legitimate. This can lead to compromised systems and/or exposed personal information, which can lead to further exposure of friends, family, and the victim’s organization.
Defeating Email Phishing:
- Is the company logo/banner/design slightly off?
- Would this person/company normally be sending you an email?
- Should they already have the information they are asking for?
- Never open unsolicited attachments
- Legitimate Companies should never ask sensitive information through email
- Use other methods to confirm the communication
Vishing
Voice phishing is growing in popularity and just like other types of phishing, vishing can be automated making it a dangerous tool. Attack examples include an “FBI” automated message, “IRS” tax refund/payment notification, or as a call from your local home improvement company. When attackers get on the line with their target they present a well thought out and engaging backstory to hook their victims. Impersonation is used in most vishing calls; attackers will impersonate IT staff, management in your company, and HR to appear official.
Defeating Vishing:
- Ask the caller to provide information only you and they would know to ensure the caller’s identity
- Never give sensitive information over the phone
- If the call is suspicious, contact someone close to the individual, or through other means
- Offer to call the individual back at the number in your staff/corporate directory, or at the number listed on the legitimate website

Smishing
Smishing sends texts to the targets phone in hopes of them clicking a malicious link, downloading malware, or returning sensitive information. Texts follow email phishing outlines and can be identified similarly. Many victims fall for smishing because they are unaware of the tactic and more trusting of texts. Don’t trust it more just because it’s a text message.
Defeating Smshing
- Never provide sensitive information over text message
- Would this person/company normally be sending you a text or make direct requests?
- Use alternative methods to confirm the communication is actually from the real person.
- Avoid following random links
- If you are unsure, reach out to your security team, or the communicating company
- Do not call the number that texted you
Spear-phishing, Whaling & Campaigns
Most individuals come into contact with phishing campaigns. The goal of campaigns are to reach as many people as possible and hope for a hit. Whereas, spear phishing and whaling are techniques aimed at selected groups of individuals and executives. These are well planned, crafted, and executed, and shouldn’t be taken lightly. They aim to compromise victims with privileged access to systems, accounts, and resources. Victims typically don’t have the time to review these carefully crafted emails highly specific to the target and fall for the trap.
Defeating Spear-phishing and Whaling
- Report suspicious emails looking for information to security
- Verify communication with the contact through other methods
- Attackers often impersonate colleagues, friends, and family
- Always assume you’re a target
- Opt for face to face meetings for confirmation of requests when possible (online or in person)
Pretexting
Pretexting is a more focused form of social engineering where attackers use detailed and convincing backstories to gain access to systems or information. This method often involves impersonating someone in a position of authority or a trusted entity to manipulate victims.
Defeating Pretexting:
- Avoid forwarding requests to subordinates and others asking them to 'take care of this' as this may convey legitimacy to the fraudulent request.
- Confirm any backstory by contacting the relevant person or office directly.
- Be suspicious of anyone asking for credentials, financial information, or access to systems.
- Verify the legitimacy of requests, whether they involve money transfers, accessing login portals, or providing sensitive information.
- Would this person/company normally be sending you a text or making direct requests?
- Use alternative methods to confirm the communication is actually from the real person.
For more information [external link to Crowdstrike.com content]
 This post is presented by the GW IT Cybersecurity Risk and Assurance team.
This post is presented by the GW IT Cybersecurity Risk and Assurance team.
#SecuringGW is a shared responsibility, so if you see something, say something. Report suspicious digital activities, including phishing emails, to abuse[@]gwu.edu.
IT Support Questions? For IT support, please contact the Information Technology Support Center at 202-994-GWIT (4948), ithelp[@]gwu.edu, or visit ithelp.gwu.edu




