
Last week the world was shocked by images of a blood red Daldykan River in central Russia (Figure 1). The cause of the unnatural coloration was the spillage of slurry over a filtration dam near the Russian city of Norilsk. The economy of Norilsk is dominated by mineral extraction and processing, with the mines and factories around the city producing 13% and 44% of the world supply for Nickel and Palladium respectively.[1] This makes Norilsk an economic powerhouse, however also gives Norilsk Nickel, the operator of the various mines around the city, a very powerful influence on the political operation of the city as well as the media.
While the spill occurred around September 5, Norilsk Nickel did not admit responsibility for the spill for nearly a week, even publishing pictures on their website of the Dalydykan River in “regular condition and show[ing] the natural color,” on September 8th. [2] It was only after significant exposure on social media, as well as in the world media, that the company finally took responsibility, issuing a statement that “”On the 5th of September after abnormal heavy rain, overflow of one of the dikes occurred, and [contaminated] water entered Daldykan River.”[3] However, the company insists that there is no danger to humans or river flora / fauna and that they were taking steps to improve safety precautions for future incidents.
Heavy industrial pollution is not a new issue for Norilsk, which has often been cited as one of the most polluted cities on the planet.[4] In fact pollution had reached such high levels that in 2010 Vladimir Putin threatened to heavily fine Norilsk Nickel if steps weren’t taken to modernize the plants and reduce pollution.[5] Norilsk Nickel has pledged to invest over $3.5 billion in plant upgrades by 2020, a welcome step for residents who suffer from the toxic pollutants in the air.
These steps being taken to modernize and reduce pollution are a good sign, however this most recent spill shows that the Arctic region is still extremely vulnerable to environmental contamination. The denial of responsibility for the spill by Norilsk Nickel is a perfect example of the worrying lack of strict governance in the region. The isolated nature Norilsk (Figure 2), with restricted access to industrial sites is indicative of the lacking environmental of oversight in the Arctic. Moreover, the companies operating in the area are not motivated to report spills, admit liability, and pay expensive cleanup costs, leaving it up to the media or civil-society to investigate these occurrences. Without the intense Social Media reaction to the ‘red-river of Norilsk,’ and its dramatic pictures, there is little doubt that the spill would have been swept under the rug or denied further.
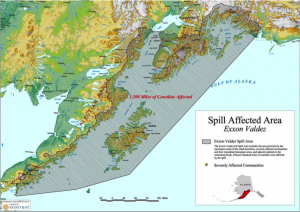
Unfortunately, this reaction to environmental disasters in the Arctic is not limited to Russia. Following the 1989 Exxon Valdez spill in Alaska, and up until present day, Exxon Mobil has tried to downplay the amount of oil spilled, and the amount of oil leftover in the area after cleanup.[6] The company was still involved in legal battles fighting against the responsibility for continuing environmental damage in 2006.[7] However, studies have shown that the vast area affected by the spill (Figure 3) has not fully recovered, both in terms of fauna population levels, and economic output.[8] Again, the remote nature of the Arctic and the fragility of the ecosystems in the region amplify the magnitude of spills, while the remote nature of the region with its relatively small populations and weak governance lessen the motivation for polluters to take responsibility. As oil exploration and general resource exploitation in the Arctic grows, we can expect more incidents like the Valdez and the Daldykan River. How regional actors respond to these inevitable disasters will help define the progress sustainable development in the Arctic.
References:
[1] http://www.nornik.ru/en/investor-relations/fact-sheet
[2] http://www.nornik.ru/en/newsroom/news-and-press-releases/news/the-daldykan-river-photo-the-river-and-its-mainstream-are-in-regular-condition-and-show-the-natural-color
[3] http://www.cnn.com/2016/09/12/world/russia-red-river-siberia/
[4] http://www.blacksmithinstitute.org/the-2007-top-ten-of-worst-polluted-places.html
[5] https://www.theguardian.com/cities/2016/sep/15/norilsk-red-river-russias-most-polluted-city-clean
[6] http://www.adn.com/economy/article/size-exxon-spill-remains-disputed/2010/06/06/
[7] http://www.abc.net.au/news/2006-05-17/exxon-valdez-oil-spill-still-a-threat-study/1755518
[8] http://publish.wm.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1020&context=caaurj

niceee