By Dominique A. Piñeiro, MA Media and Strategic Communication ’23
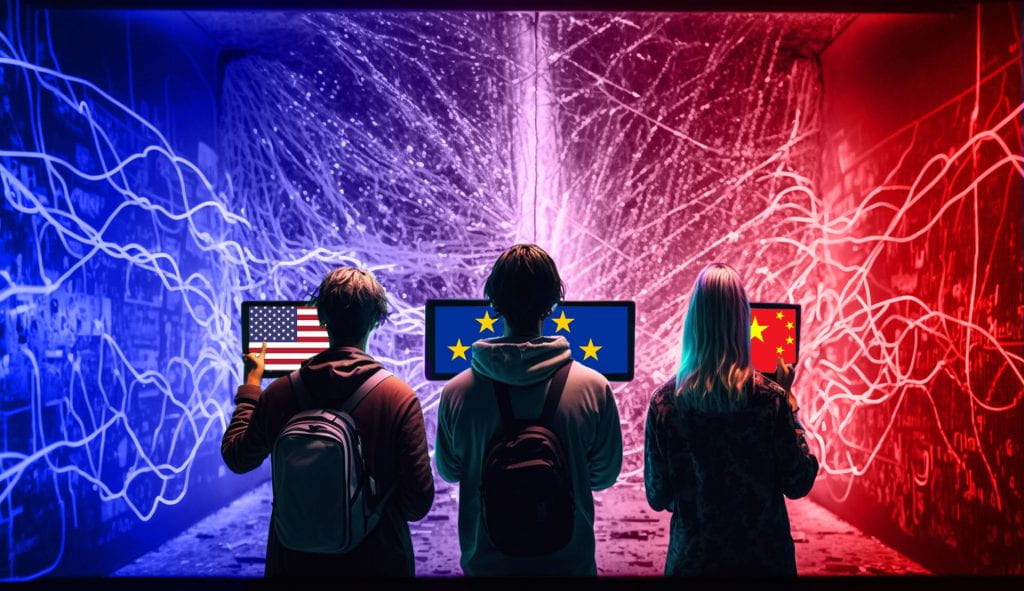

concept of the “TriNet,” representing a narrative contest among the
U.S., the European Union (E.U.), and China. Each international player
seeks to promote its approach to Internet governance and digital
policies on the world stage. The image portrays three distinct data
streams flowing through an ethereal cyberspace landscape filled with
vibrant neon colors and intricate geometric patterns. (Dominique A.
Piñeiro via MidJourney)
The Internet is evolving into a “TriNet” model, with three distinct approaches: China’s strict government control, the E.U.’s focus on data protection and privacy, and the U.S.’s market-driven approach emphasizing profit and competition. This shift alters the Internet’s original principles of openness and accessibility, raising concerns for human rights, democracy, and the free flow of information.
The “TriNet” model represents a narrative contest among the U.S., the European Union (E.U.), and China. Each player seeks to promote its approach to Internet governance and digital policies on the world stage. This narrative contest involves asserting the superiority of their respective models, with the opportunity to shape international norms and influence other countries’ adoption of similar frameworks.
The U.S. promotes a free and open web, believing global Internet access would spread rights, freedom, and democracy. However, the U.S. model is primarily driven by private businesses, leading to the rise of tech giants like Amazon, Apple, Alphabet, Meta, and Microsoft. These companies accumulate profits and power without sufficient regulations to protect users, potentially undermining American democracy and other countries.
A striking example is Meta’s (formerly Facebook) role in the 2017 Rohingya crisis in Myanmar, where its platform was used to incite violence and discrimination. Although not intentionally designed for this purpose, Meta’s focus on engagement and data collection contributed to spreading harmful content. In the Myanmar example, the U.S. effectiveness in influencing global Internet policies might be hindered by the issues arising from the largely unregulated tech industry and increasing calls for data privacy and antitrust regulations, which the E.U. is happy to lead.
The E.U.’s alternative also seeks to spread rights, freedom, and democracy. Still, it emphasizes data privacy, with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) harmonizing data privacy laws across member states and offering individuals greater control over personal data. While not explicitly addressing human rights, GDPR provisions can prevent the misuse of data that leads to situations like Myanmar’s crisis. The GDPR sets a worldwide data privacy standard, contrasting with the U.S.’s fragmented approach, which includes sector-specific regulations like HIPAA and COPPA.
While the E.U. model and GDPR significantly improve data protection and privacy, there are also potential disadvantages. A specific example would be how GDPR imposes compliance requirements on businesses, which can be interpreted differently by E.U. member states, and is an expensive process, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises.
China’s approach contrasts sharply with the U.S. and E.U. In a 2000 speech, President Bill Clinton questioned China’s ability to control the Internet effectively:
“Now, there’s no question China has been trying to crack down on the Internet – good luck. That’s sort of like trying to nail jello to the wall. But I would argue that their effort to do that proves how real these advances are and how much they threaten the established order of things, especially the government’s tight information control.”
His remarks were meant to convey that the Internet’s decentralized nature makes it difficult for governments to control or censor information effectively. Ironically, his statement foreshadowed what was possible. The Great Firewall of China, or Golden Shield Project, demonstrates a sophisticated censorship and control system. China emphasizes sovereignty and states’ rights in information and communication, enacting policies to realize its vision.
China exports its internet censorship and surveillance technology to other countries, promoting its regulated Internet model worldwide. Since the 2021 coup d’état, Myanmar has been increasingly cutting off its population from the Internet, causing concern that the regime could become a model for other authoritarian governments if not economically crippled.
China’s strict government-controlled Internet model could be framed as a solution to promoting a harmonious society. The government would control information dissemination significantly, limiting public knowledge of ongoing events and potentially suppressing information. This type of control could appeal to illiberal democracies and autocrats alike. It’s also important to note that a highly controlled internet can monitor and target specific ethnic or religious groups by a government to identify, suppress, or persecute vulnerable populations, potentially leading to or worsening a genocide.
The U.S. and E.U. value free speech and human rights and view China’s controlled and regulated Internet model negatively. However, China’s economic and technological prowess could attract some nations seeking to emulate its success or strengthen political control over their populations. China’s influence may grow in authoritarian countries or those seeking alternative models to Western Internet governance.
The evolving “TriNet” model’s distinct approaches—China’s stringent control, the E.U.’s emphasis on data protection and privacy, and the U.S.’s profit-driven strategy—raise concerns over human rights, democracy, and information flow. The Rohingya crisis in Myanmar exemplifies how American tech giants’ practices and China’s internet control technology can have devastating consequences for vulnerable populations. While the U.S. approach to the Internet has flaws, it’s vital to contemplate the ramifications of a world where China sets the standards for digital governance. A free and open internet enables individuals to express their opinions, share ideas, and access diverse perspectives without fear of censorship or persecution.
The full report is available.
The opinions expressed in this blog are those of the author. They do not express the views of the Institute for Public Diplomacy and Global Communication or the George Washington University.
In addition, the opinions and characterizations in this piece are those of the author and do not necessarily represent those of the U.S. Government.




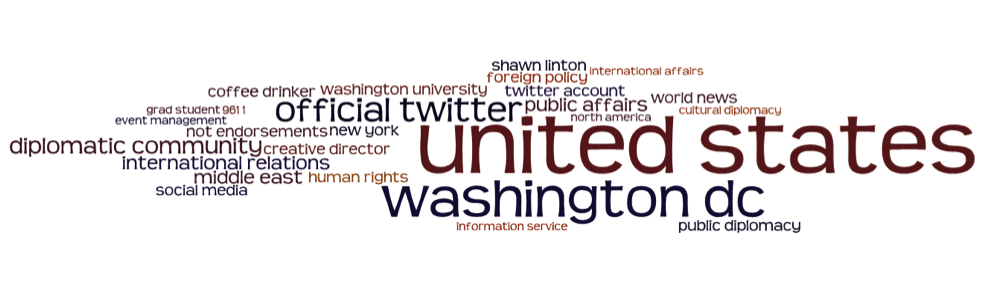
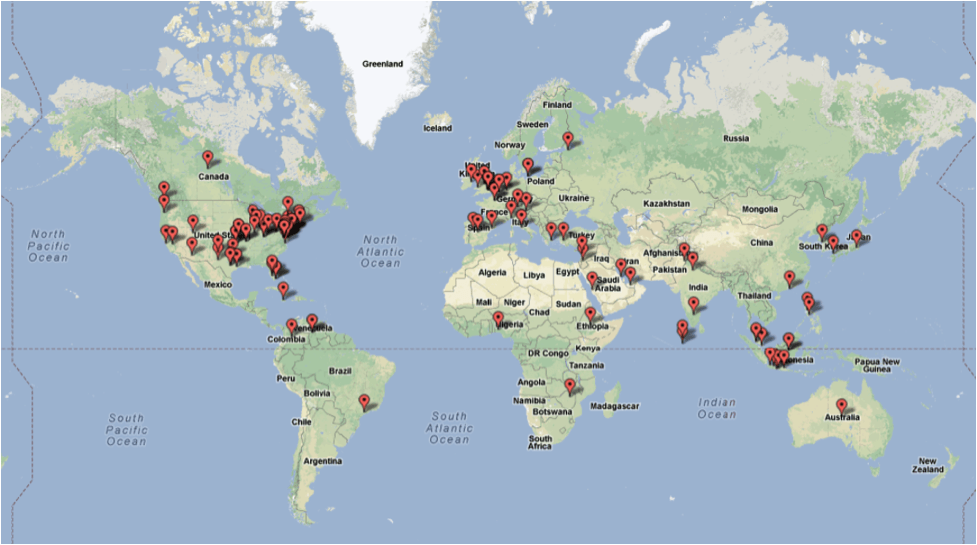













 On January 5-6, while India and Pakistan faced each other on the cricket pitch, teams of exchange program alumni from India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh engaged in
On January 5-6, while India and Pakistan faced each other on the cricket pitch, teams of exchange program alumni from India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh engaged in  secured the first live phone interview with a Malawian president as a result of his U.S. program experience. In his words: “one thing I learned while covering the elections is that the American President is always scrutinized by the public. Immediately I arrived home I got in touch with our ‘White House’ to have the President answer questions from the public. I am proud to announce that on December 31, I was the first Malawian journalist to have a live phone interview with the President where people posed questions to [him], a thing that has never happened before in my country.”
secured the first live phone interview with a Malawian president as a result of his U.S. program experience. In his words: “one thing I learned while covering the elections is that the American President is always scrutinized by the public. Immediately I arrived home I got in touch with our ‘White House’ to have the President answer questions from the public. I am proud to announce that on December 31, I was the first Malawian journalist to have a live phone interview with the President where people posed questions to [him], a thing that has never happened before in my country.” Jerusalem: The board game Monopoly has proven a potent tool in fostering the entrepreneurial spirit among Palestinian youth, while simultaneously introducing a mainstay of American culture.
Jerusalem: The board game Monopoly has proven a potent tool in fostering the entrepreneurial spirit among Palestinian youth, while simultaneously introducing a mainstay of American culture.  In the lead-up to the U.S. Presidential Inauguration, Consulate Hong Kong began a social media project that included photos, videos and travelling cardboard cutouts of President Obama and the First Lady.
In the lead-up to the U.S. Presidential Inauguration, Consulate Hong Kong began a social media project that included photos, videos and travelling cardboard cutouts of President Obama and the First Lady.  The U.S. Consul General in Munich spoke to students and faculty of “Berufsschule 4,” an off-the-beaten-track school in Nuremberg. He addressed U.S.-German relations, the U.S. presence in Bavaria, and economic and commercial ties, and tackled tough questions about car emissions, Guantanamo, gun control, and social media topics. The
The U.S. Consul General in Munich spoke to students and faculty of “Berufsschule 4,” an off-the-beaten-track school in Nuremberg. He addressed U.S.-German relations, the U.S. presence in Bavaria, and economic and commercial ties, and tackled tough questions about car emissions, Guantanamo, gun control, and social media topics. The




















