by Kate Shriver
 First, there was Gangam Style, the epic YouTube video by South Korean pop sensation Psy that swept the world in 2012 and currently has over one billion views, making it the most viewed YouTube video of all time. Anyone who was anyone made a spinoff or parody of their own.
First, there was Gangam Style, the epic YouTube video by South Korean pop sensation Psy that swept the world in 2012 and currently has over one billion views, making it the most viewed YouTube video of all time. Anyone who was anyone made a spinoff or parody of their own.
Now, there is the Harlem Shake. Here’s the premise: in an approximately 30 second long video a single person dances for roughly 10-20 seconds on their own (usually in a mask or helmet of some sort) while everyone else around them carries on with their own business, essentially ignoring the lone dancer. When the music “drops,” the video cuts to everyone in the room dancing basically just any way they want, though it typically involves a lot of gyrating, hip thrusting and a variety of masks, costumes and other props. The accompanying music is by US artist Baauer—and depending on whom you ask—the initial video was posted in early February by a group of young men in Australia, or it was posted by these guys somewhere else.
 In reality, the Harlem Shake in its first form was a dance that characterized the New York neighborhood of the same name in the 1980s. This information aside, the modern day Harlem Shake has taken off at lightning speed with hundreds of new versions posted to YouTube every day. The craze is starting to wind down in the US and the West, though the fad has not come without a few brushes with the authorities: in the US, the FAA is investigating an incident which involves posted Harlem Shake video that appeared to show the crazy dancing taking place on a plane that was in flight. There have been reports of students being suspended for filming their own versions in school. In Australia, a group of miners were fired and reportedly banned from all mine sites after authorities discovered their Harlem Shake video, which they apparently shot while on their work site—in a mine! One of the most popular versions, with over 50 million YouTube views, was created by members of the Norwegian Army who are featured dancing around in the snow after breaking formation.
In reality, the Harlem Shake in its first form was a dance that characterized the New York neighborhood of the same name in the 1980s. This information aside, the modern day Harlem Shake has taken off at lightning speed with hundreds of new versions posted to YouTube every day. The craze is starting to wind down in the US and the West, though the fad has not come without a few brushes with the authorities: in the US, the FAA is investigating an incident which involves posted Harlem Shake video that appeared to show the crazy dancing taking place on a plane that was in flight. There have been reports of students being suspended for filming their own versions in school. In Australia, a group of miners were fired and reportedly banned from all mine sites after authorities discovered their Harlem Shake video, which they apparently shot while on their work site—in a mine! One of the most popular versions, with over 50 million YouTube views, was created by members of the Norwegian Army who are featured dancing around in the snow after breaking formation.
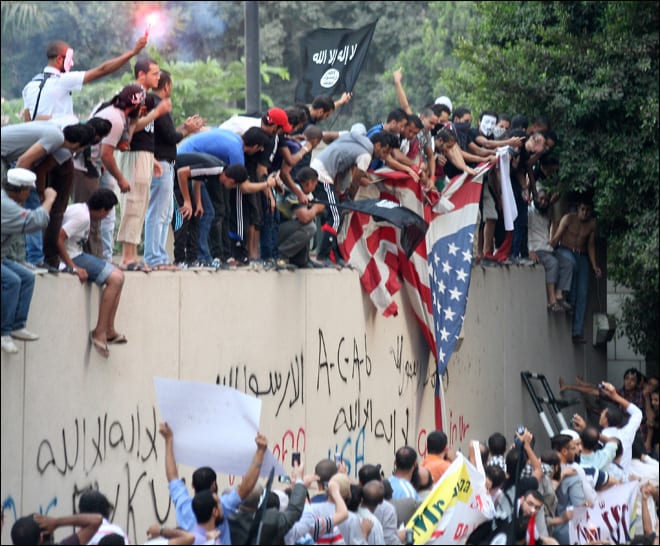
While the meme may be wearing out its popularity in the West, it is just beginning to get going in the Middle East: Cecily Hilleary of Middle East Voices (A VOA powered initiative) has compiled a list of Middle Eastern countries where the dance craze has gone viral, from Algeria to Yemen. But it is in Tunisia and Egypt—the hotbeds of the Arab Spring—where the Harlem Shake meme is taking on new meaning. The dance seems to have morphed into a form of social protest against the respective governments who have, in response, cracked down hard on some of those who created the videos.
 In Tunisia, where there has been a split between secularists and ultra conservative Salafis since the fall of the regime of Zine El Abidine Ben Ali over 2 years ago, a group of students at a high school in Tunis filmed a version of the Harlem Shake in which some students danced in their underwear, dressed up as Salafis with fake beards, or as Gulf emirs (among other costumes). The provocative nature of the dancing caught the attention of the Salafis, who decried the video as indecent. Minister of Education Abdellatid Abid, angrily denounced the video as indecent also, and ordered an investigation of the school’s principal. Skirmishes have erupted elsewhere in Tunisia as conservative Muslims attempt to stop youth from partaking in other Harlem Shake videos—with one student in coastal Mahdia purportedly receiving 12 stitches on his head after being beaten in one such clash.
In Tunisia, where there has been a split between secularists and ultra conservative Salafis since the fall of the regime of Zine El Abidine Ben Ali over 2 years ago, a group of students at a high school in Tunis filmed a version of the Harlem Shake in which some students danced in their underwear, dressed up as Salafis with fake beards, or as Gulf emirs (among other costumes). The provocative nature of the dancing caught the attention of the Salafis, who decried the video as indecent. Minister of Education Abdellatid Abid, angrily denounced the video as indecent also, and ordered an investigation of the school’s principal. Skirmishes have erupted elsewhere in Tunisia as conservative Muslims attempt to stop youth from partaking in other Harlem Shake videos—with one student in coastal Mahdia purportedly receiving 12 stitches on his head after being beaten in one such clash.
A video linked to the original Tunis high school Harlem Shake video is titled “The Harlem Shake: Attacked by Salafis Edition” which appears to show a schoolyard where students are about to do the dance, and are then attacked by Salafis. In some of the skirmishes the Salafists have reportedly shouted at the students “Our brothers in Palestine are being killed by Israelis, and you are dancing.”
Only a few days ago a mass protest/Harlem Shake dance was planned in Tunis in front of the Ministry of Education. Thousands said they would participate, but the rainy weather appeared to have dampened the turnout, with only a few dozen students taking part in the protest with shouts of “freedom, freedom.” In a Washington Post report, students stated their own reasons for participating in the dance: one said the dance represented a way to vent and take a break from the stresses of the past year, and another reported that he wanted to take advantage of the newfound freedoms thanks to the revolution after years of harassment and repression. In additional reporting on the mass protest, a student said he was there to make the minister of education understand that he cannot stop the dancing – “This policy of suppressing rebellious spirit is no longer acceptable.” The initial video and the backlash have only served to produce even more Harlem Shake videos, and the meme and its meaning continue to flourish in Tunisia.
 In Egypt, where there are strict public indecency laws, four pharmaceutical students were arrested after posting a video of themselves doing the dance semi-naked in a middle-class Cairo neighborhood. Students in Egypt have also posted videos of the Harlem Shake being done in front of the Pyramids (it is unclear whether the Pyramid video is the same one that resulted in the arrests).
In Egypt, where there are strict public indecency laws, four pharmaceutical students were arrested after posting a video of themselves doing the dance semi-naked in a middle-class Cairo neighborhood. Students in Egypt have also posted videos of the Harlem Shake being done in front of the Pyramids (it is unclear whether the Pyramid video is the same one that resulted in the arrests).
Following the arrests of the four students, somewhere between 70 and 400 protesters showed up outside
the headquarters of the Muslim Brotherhood in Cairo to stage a Harlem Shake dance/protest. The dance was organized to be a peaceful protest of the ruling party and President Mohammed Morsi, and a lighthearted moment in an Egypt that is still reeling from its transformation. A unique twist in the Egypt story: a member of the Muslim Brotherhood created his own Harlem Shake video in response to the protest, in which he and other people wear masks featuring the faces of opposition party members. The video has apparently since been taken down.
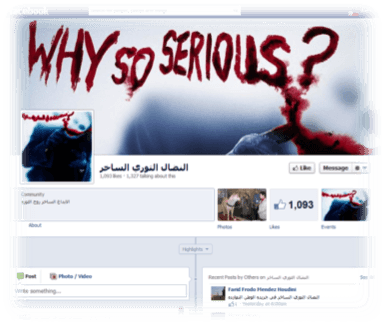
What is particularly interesting about the way the Harlem Shake is being used in Egypt, is that the protest outside the Muslim Brotherhood headquarters was organized by a newly formed group called “The Satiric Revolutionary Struggle” which has
its own Facebook page with over 1,000 likes. The Verge reports that the group was started by 17 year old Mahmoud Tabei and three of his friends so that they could work on making political statements through humorous demonstrations. Tabei said that he had seven friends who died in the Arab Spring violence in Egypt and that another of the aims of the newly formed group is to raise morale and “refresh minds.” The next event the group is working on is a marathon that will start at the headquarters of the National Democratic Party (the party of deposed autocrat Hosni Mubarak), and end at the Muslim Brotherhood’s headquarters. The Verge writes that “it’s a path meant to symbolize Egypt’s political trajectory from Mubarak to Morsi. Its message, according to Tabei, should be clear: ‘They are the same. Nothing has changed.’”
So what does all of this mean for cultural public diplomacy? It appears that the Harlem Shake meme was an inadvertent export of Western culture (particularly U.S. culture) that hit the Middle East and transformed from something that was initially fun and lighthearted, into something more meaningful and useful to politically active youth, especially in Egypt and Tunisia.
Can the US government or an NGO or another some other PD actor harness the power and popularity of the meme in any way? Perhaps a rapid response digital media team at the State Department could message words of support for the dancers citing freedom of expression? It certainly doesn’t look good for the either the Tunisian government or the Egyptian government to crack down violently on the dancers, so that is something that the State department could monitor and then respond to if necessary.
It could also be true that this type of super fast social media movement is impossible to control or use in any way for cultural diplomacy. It seems that in the ever important short/mid/long term goals of public diplomacy, and particularly cultural diplomacy, that this sort of meme presents an “instant” goal of some sort—something that can be recognized and addressed.
 Where a real opportunity lies is with the newly formed Satiric Revolutionary Struggle group founded by an Egyptian teenager and his friends. This is a group with robust backing on Facebook, and something that could be assisted with support from the USG directly, perhaps through a program that brings comedy troupes or political satirists from the US to Cairo to teach the group some of the “tricks of the trade.” Or an NGO or other organization could reach out to the group and show them similar skills they could use, as well as other popular media they could use in order to satirize the government. It is obviously still quite risky to criticize the government in Egypt, so the newly formed group should also receive training on how to avoid conflict, etc.
Where a real opportunity lies is with the newly formed Satiric Revolutionary Struggle group founded by an Egyptian teenager and his friends. This is a group with robust backing on Facebook, and something that could be assisted with support from the USG directly, perhaps through a program that brings comedy troupes or political satirists from the US to Cairo to teach the group some of the “tricks of the trade.” Or an NGO or other organization could reach out to the group and show them similar skills they could use, as well as other popular media they could use in order to satirize the government. It is obviously still quite risky to criticize the government in Egypt, so the newly formed group should also receive training on how to avoid conflict, etc.
Perhaps the most important point to consider in this case is the US and its foreign policy remain largely unpopular in much of the Middle East—so any overt help given by the USG could be outright rejected, or worse: it could be seen as foreign meddling likely to result in a total shut down of whatever initiative it was trying to assist with in the first place. Thus the name of the game is “indirectness” – assistance in the form of things the group may actually want or need (e.g. a good piece of technological equipment to assist with video production or editing).
Sure, the Harlem Shake is probably not a highlight of US culture that the government would choose to export: it is not a gem like jazz or classical dance or paintings. But it is something that has a wide appeal to a huge youth population in the still evolving Middle East, and it is something the USG could potentially use to provide “helping” public diplomacy.
Kate Shriver is a graduate student in the International Affairs program at the George Washington University with a focus on the Middle East.
The above post is from Take Five’s new Student Perspective series. Graduate students studying Cultural Diplomacy as Communication at the George Washington University are encouraged to think about themes such as youth, gender, health, climate, free press, and democracy, and write on how these themes relate to cultural diplomacy and to communication. The posts involve thoughtful commentary on the writer’s chosen theme, linking to class readings and discussions.


































